Bio an Action Potential Can Best Be Described
It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. An action potential is the result of a very rapid rise and fall in voltage across a cellular membrane with every action potential impulse similar in size.
Action Potential Biology For Majors Ii
Quizlet flashcards activities and games help you improve your grades.

. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 1257. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. Saltatory conduction stimulus for the next action potential.
An action potential requires an influx of positive ions to produce. Na channels open at the beginning of the action. BIO 201 - Action Potential study guide by pclindse includes 34 questions covering vocabulary terms and more.
What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 7. The action potential can be classified into five stages. Action potentials are regenerated along an axon as one action potential serves as the A.
In some neurons a single action potential can be induced by the offset of a hyperpolarizing stimulus Fig. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like What is an action potential AP The voltage gated channels that allow an AP to occur are located in an _____ Why can actions potentials only move one way along the axon. Propagation of the Action Potential.
Steps in action potential. It is the membrane potential of a neuron at rest. If the threshold of excitation is reached all Na channels open and the membrane depolarizes.
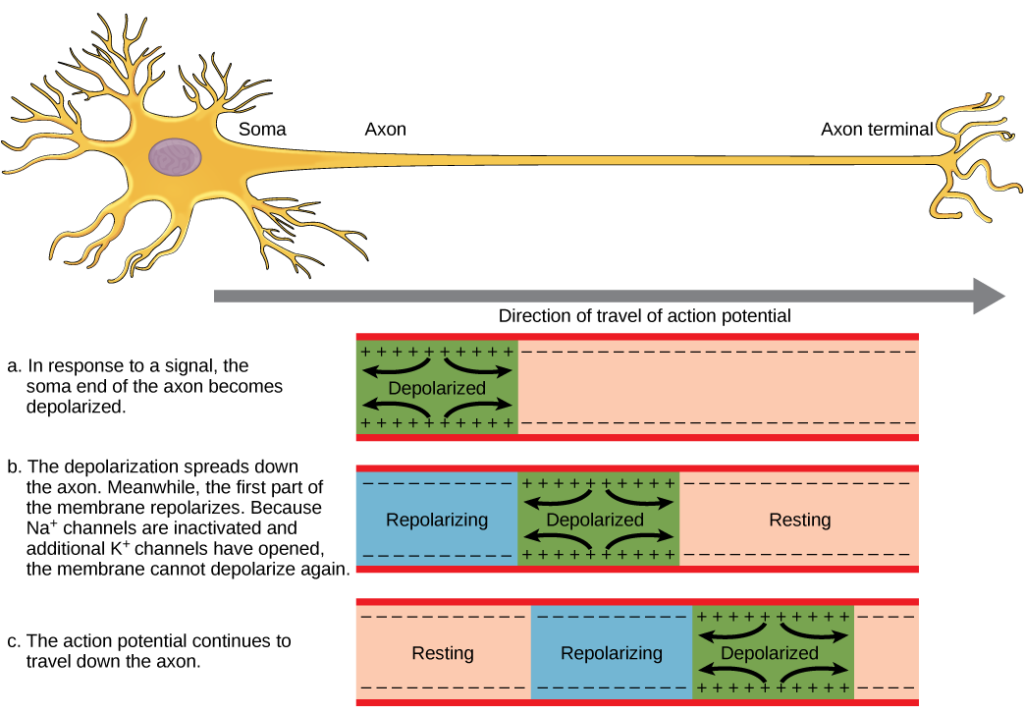
In order to understand this spreading phenomenon commonly referred to as propagation it is important to understand three concepts. As an action potential nerve impulse travels down an axon there is a change in electric polarity across the membrane of the axon. Stay tuned to BYJUS to learn more NEET questions.
This phenomenon is called anodal break excitation or. These local currents may occur at the site of. Key facts about the action potential.
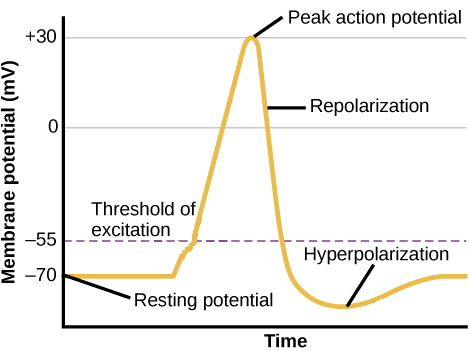
During an action potential and few milliseconds after there is a period of time where it is difficult or impossible to stimulate that region of a neuron again. The change in the membrane voltage from -70 mV at rest to 30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in.
As covered in Chapter 1 the action potential is a very brief change in the electrical potential which is the difference in charge between the inside and outside of the cell. An action potential AP is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. Na inactivation gate opens activation gate is closed.
An action potential occurs when a portion of the membrane rapidly depolarizes and then repolarizes again to the original resting state. Monosynaptic reflex stimulus for the next action potential. A stimulus from a sensory cell or another neuron causes the target cell to depolarize toward the threshold potential.
Action potentials are generated when voltage-gated sodium channels open as a result of the passage of local electrical currents across the membrane. In response to a signal from another neuron sodium- Na and potassium- K gated ion channels open and close as the membrane reaches its threshold potential. That property is called the excitability.
Permeability of the membrane translates to the action of the ion channels in allowing certain ions to enter the cell which would otherwise not be possible in the normal resting stage. -need to reach threshold potential around -55 mV. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential.
The functions of the nervous systemsensation integration and responsedepend on the functions of the neurons underlying these pathways. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. The process is initiated by a threshold level stimulus such as a nearby change in membrane potential threshold potential local potential.
A depolarisation produced by a generator potential at a sensory ending. An action potential is defined as a sudden fast transitory and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. The action potential propagates in the direction of the dendrite.
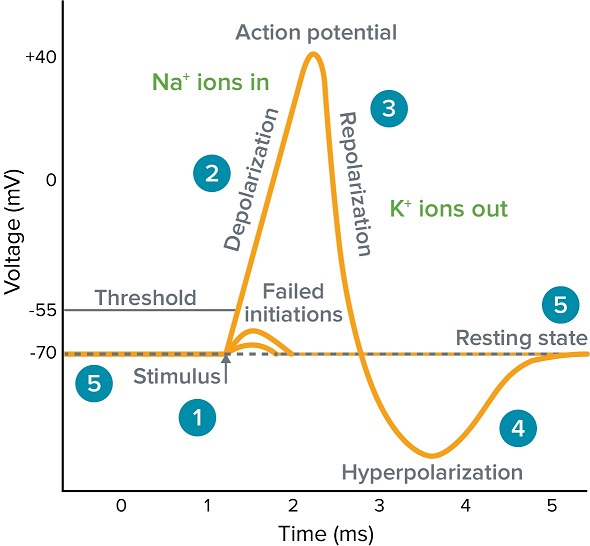
Na_ channel proteins have 2 gates K_ 1 voltage gated channel proteins. The response of a nerve or muscle cell to an action potential can vary according to how frequently and for what duration the action potentials are fired. At the peak action potential K channels open and K begins to leave the cell.
The ultimate goal of the action potential is to spread along the membrane inducing changes in voltage-gated proteins thus allowing ions to follow their gradients and generate electrical current. Action potential starts with the resting potential. Cells in the nervous system that use electrical and chemical signals to receive process and transmit information.
The action potential is said to be all-or-nothing because it occurs only for sufficiently large depolarizing stimuli and because its form is largely independent of the stimulus for suprathreshold stimuli. The change in the membrane voltage from 70 mV at rest to 30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change. Action potential stimulus for the next action potential.
However the underlying current flow is perpendicular to the axonal membrane and is mediated by ion channels. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs. -requires a strong depolarizing event.
It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. Excitatory postsynaptic potential stimulus for the next action potential. To understand how neurons are able to communicate it is necessary to describe the role of an excitable membrane in generating these signals.
An aspect of an organisms environment that is detectable by a neuron. - This can be described as the Unidirectional propagation of the AP. At threhsold about -55mV many Na voltage-gated channels open.
It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. These ion channels are activated through the sensing of the electrical field. An action potential is described as a sudden and spontaneous change or reversal in the membrane potential above a threshold value due to increased permeability of the cell membrane.
Dendrites and cell. During the action potential the electrical potential across the membrane moves from a negative resting value to a positive value and back.

Action Potential The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy

A Schematic Of An Action Potential When A Stimulus Is Applied An Download Scientific Diagram
What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart Membrane Potential Molecular Devices
No comments for "Bio an Action Potential Can Best Be Described"
Post a Comment